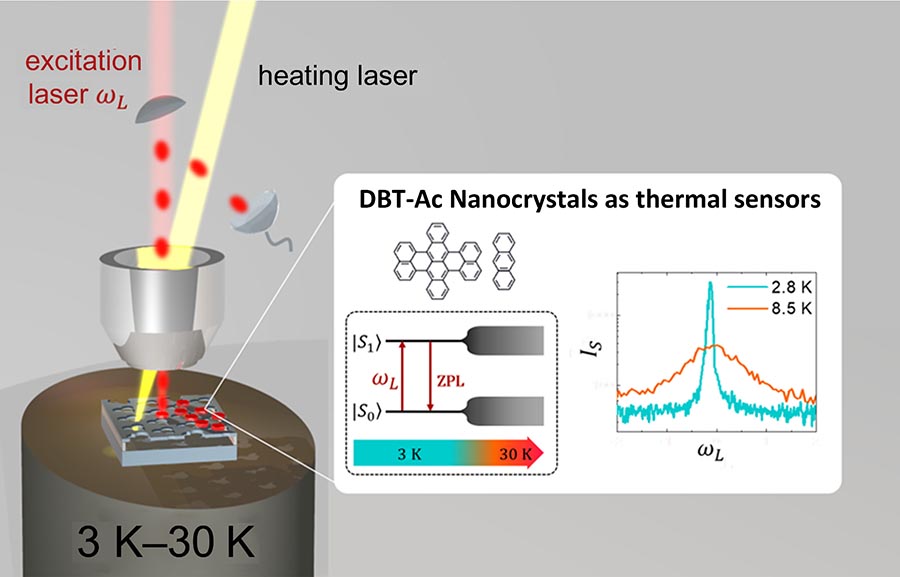
 Taking the temperature of a sample can be tricky—especially in the regimes of the very small and the very cold. The smaller the sample, the greater the influence the thermometer itself may exert on the measurement. And in the ultracold regime, even tiny amounts of heat can significantly alter the temperature reading.
Taking the temperature of a sample can be tricky—especially in the regimes of the very small and the very cold. The smaller the sample, the greater the influence the thermometer itself may exert on the measurement. And in the ultracold regime, even tiny amounts of heat can significantly alter the temperature reading.
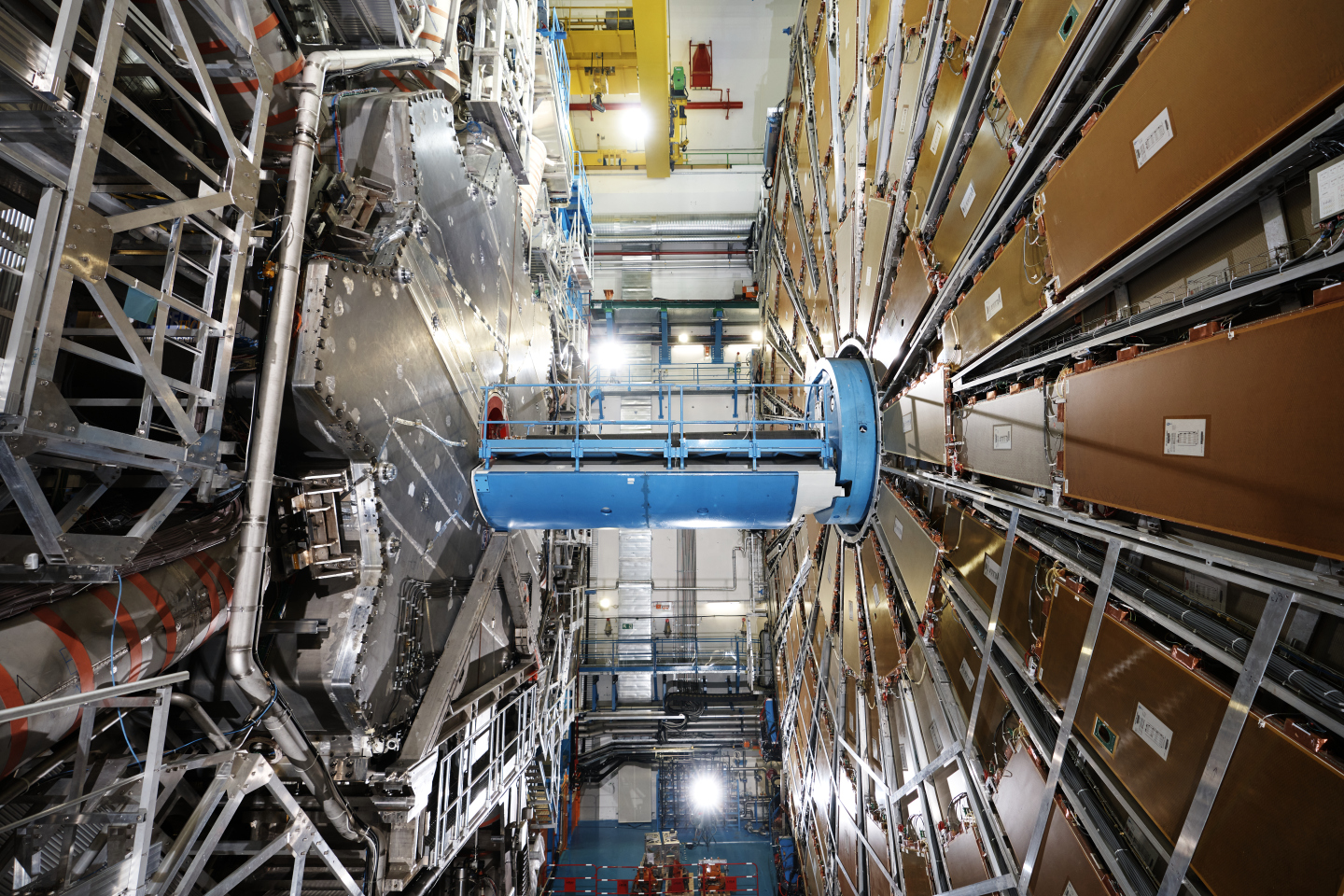 Binding together quarks into protons, neutrons and atomic nuclei is a force so strong, it’s in the name. The strong force, which is carried by gluon particles, is the strongest of all fundamental forces of nature – the others being electromagnetism, the weak force and gravity. Yet, it’s the least precisely measured of these four forces. In a paper just submitted to Nature Physics, the ATLAS collaboration describes how it has used the Z boson, the electrically neutral carrier of the weak force, to determine the strength of the strong force with an unprecedented uncertainty of below 1%.
Binding together quarks into protons, neutrons and atomic nuclei is a force so strong, it’s in the name. The strong force, which is carried by gluon particles, is the strongest of all fundamental forces of nature – the others being electromagnetism, the weak force and gravity. Yet, it’s the least precisely measured of these four forces. In a paper just submitted to Nature Physics, the ATLAS collaboration describes how it has used the Z boson, the electrically neutral carrier of the weak force, to determine the strength of the strong force with an unprecedented uncertainty of below 1%.


 Someone waking up inside of WEST, the French tokamak located barely one kilometer away from ITER, would think they had been transported into an alien spaceship—and more specifically, into the stranded star-faring vessel in the movie Alien (1979), with its strange ribcage-like walls and dull metal vertebrae. Last week, a (perfectly awake) Newsline reporter was privileged to spend a few hours inside the machine's plasma chamber, where some of the longest plasma shots in fusion history were produced.
Someone waking up inside of WEST, the French tokamak located barely one kilometer away from ITER, would think they had been transported into an alien spaceship—and more specifically, into the stranded star-faring vessel in the movie Alien (1979), with its strange ribcage-like walls and dull metal vertebrae. Last week, a (perfectly awake) Newsline reporter was privileged to spend a few hours inside the machine's plasma chamber, where some of the longest plasma shots in fusion history were produced.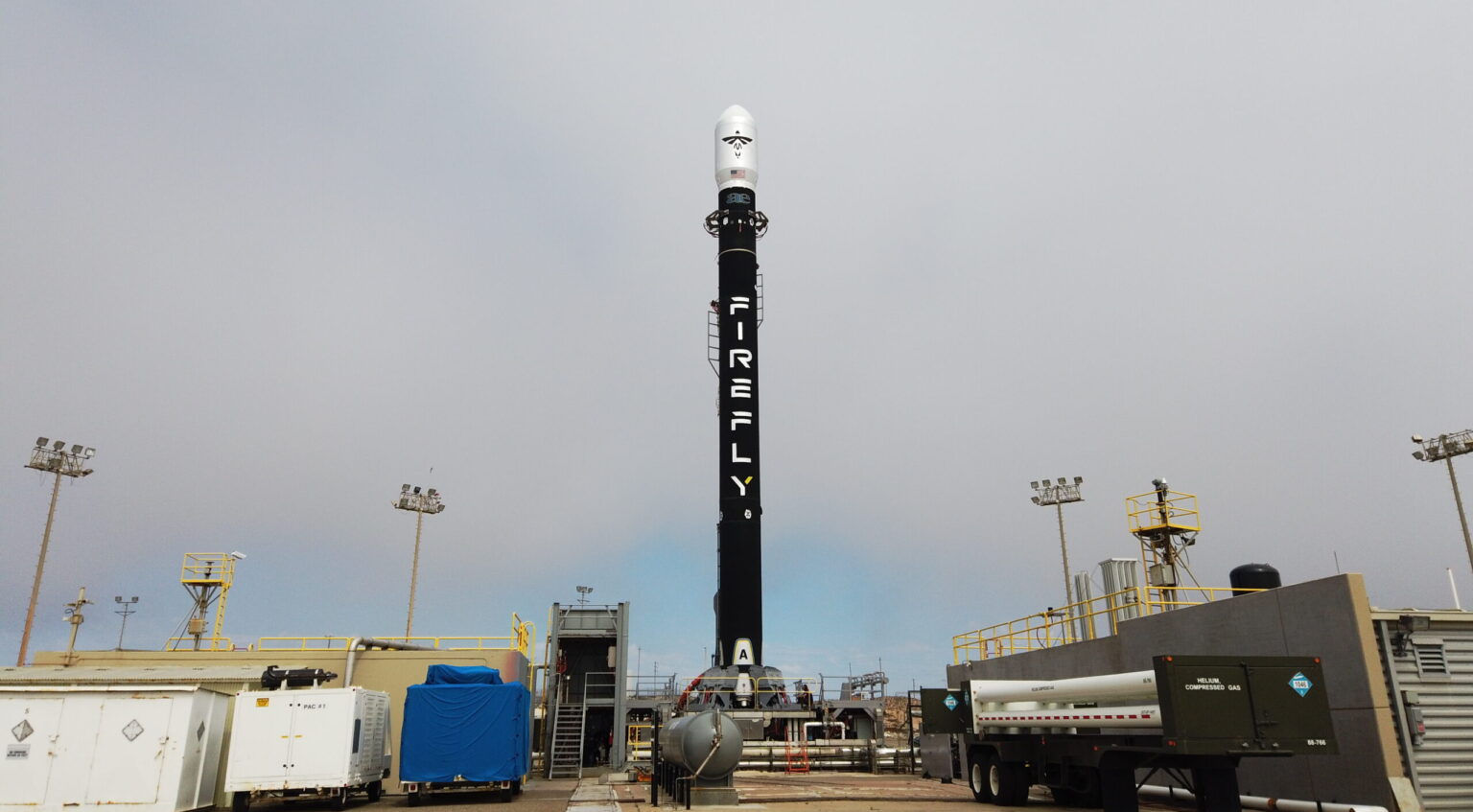 Firefly Aerospace, Inc., an end-to-end space transportation company, today announced it signed a multi-launch agreement with L3Harris Technologies for three dedicated launches on Firefly’s Alpha vehicle in 2026.
Firefly Aerospace, Inc., an end-to-end space transportation company, today announced it signed a multi-launch agreement with L3Harris Technologies for three dedicated launches on Firefly’s Alpha vehicle in 2026.  The world’s wildlife
The world’s wildlife Aston University research has shown the way forward for making renewable hydrogen and propane fuel gases from glycerol. An organic compound, glycerol is produced mainly from fats and oils and is often used in health and beauty products. With crude glycerol from biodiesel production plants cheap and abundant the researchers have explored its potential for making hydrogen gas and biopropane - pioneering work that could benefit the environment and reduce reliance on fuel imports.
Aston University research has shown the way forward for making renewable hydrogen and propane fuel gases from glycerol. An organic compound, glycerol is produced mainly from fats and oils and is often used in health and beauty products. With crude glycerol from biodiesel production plants cheap and abundant the researchers have explored its potential for making hydrogen gas and biopropane - pioneering work that could benefit the environment and reduce reliance on fuel imports. Quantum mechanics is a branch of physics that explores the properties and interactions of iparticles at very small scale, such as atoms and molecules. This has led to the development of new technologies that are more powerful and efficient compared to their conventional counterparts, causing breakthroughs in areas such as computing, communication, and energy.
Quantum mechanics is a branch of physics that explores the properties and interactions of iparticles at very small scale, such as atoms and molecules. This has led to the development of new technologies that are more powerful and efficient compared to their conventional counterparts, causing breakthroughs in areas such as computing, communication, and energy.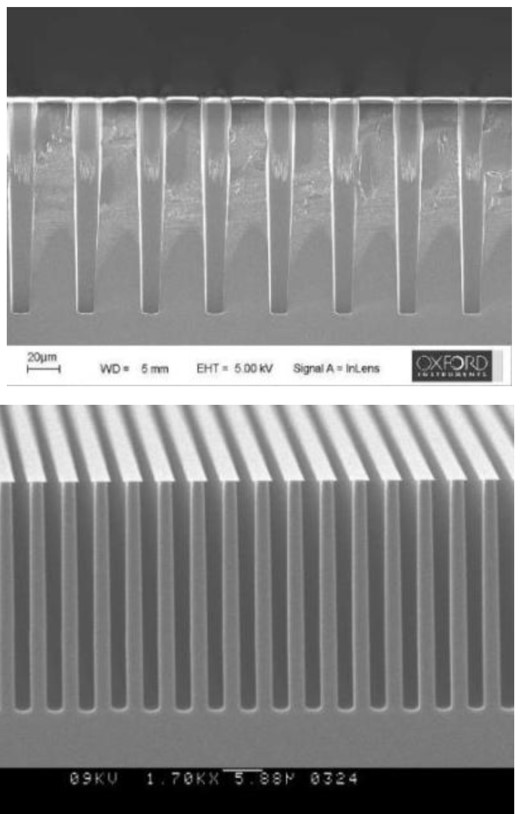 After years in R&D, a technology called cryogenic etch is re-emerging as a possible option for production as the industry faces new challenges in memory and logic.
After years in R&D, a technology called cryogenic etch is re-emerging as a possible option for production as the industry faces new challenges in memory and logic.  Structure-based designs are integral to advancing drug discovery, and in this regard, cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) has emerged as a pivotal tool for achieving high-resolution structures of proteins and protein complexes. Particularly noteworthy is its utility in elucidating the structures of protein classes that have historically resisted crystallization.
Structure-based designs are integral to advancing drug discovery, and in this regard, cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) has emerged as a pivotal tool for achieving high-resolution structures of proteins and protein complexes. Particularly noteworthy is its utility in elucidating the structures of protein classes that have historically resisted crystallization. RegO Products has unveiled its latest breakthrough: the CBE504 Series of Half-Inch Pressure Builder-Economizer Regulators. Designed to enhance cryogenic vessel operations, these regulators prioritize pressure control and product preservation.
RegO Products has unveiled its latest breakthrough: the CBE504 Series of Half-Inch Pressure Builder-Economizer Regulators. Designed to enhance cryogenic vessel operations, these regulators prioritize pressure control and product preservation.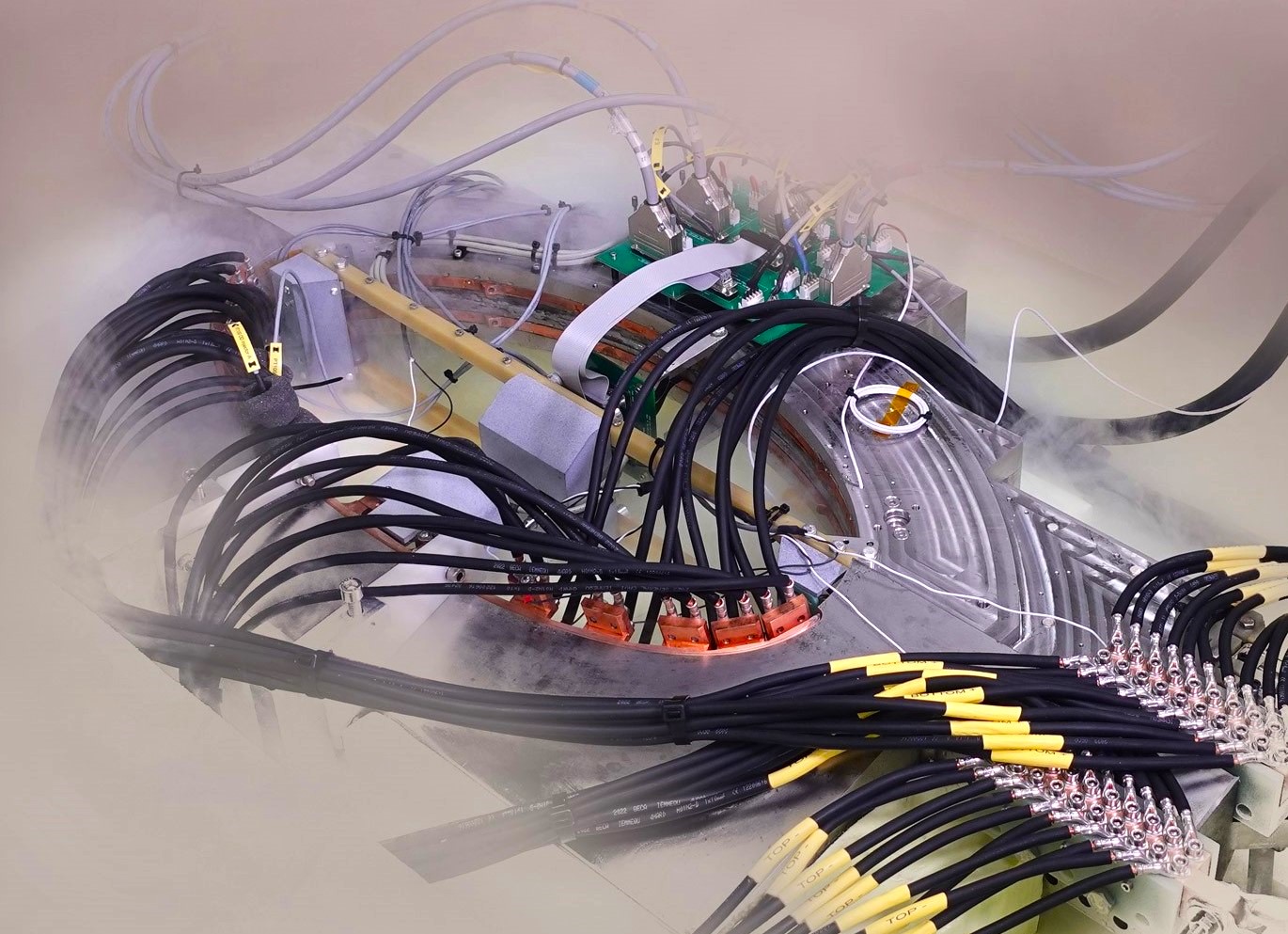 UK-based Tokamak Energy’s superconducting magnet system, which is being built to replicate fusion energy power plant forces, has passed significant milestone cryogenic tests. Creating fusion energy requires strong magnetic fields to confine and control the extremely hot hydrogen fuel, which becomes a plasma several times hotter than the center of the sun.
UK-based Tokamak Energy’s superconducting magnet system, which is being built to replicate fusion energy power plant forces, has passed significant milestone cryogenic tests. Creating fusion energy requires strong magnetic fields to confine and control the extremely hot hydrogen fuel, which becomes a plasma several times hotter than the center of the sun. In the rapidly evolving landscape of quantum technology, cryogenics is an indispensable and fascinating domain that pushes the boundaries of low-temperature physics. Harnessing the power of extreme cold, this groundbreaking field plays a pivotal role in unlocking the true potential of quantum phenomena. This field of research has its origins in the early 20th century and has since become a vital area of study for understanding quantum phenomena and developing advanced technologies like superconductors and quantum computing.
In the rapidly evolving landscape of quantum technology, cryogenics is an indispensable and fascinating domain that pushes the boundaries of low-temperature physics. Harnessing the power of extreme cold, this groundbreaking field plays a pivotal role in unlocking the true potential of quantum phenomena. This field of research has its origins in the early 20th century and has since become a vital area of study for understanding quantum phenomena and developing advanced technologies like superconductors and quantum computing.
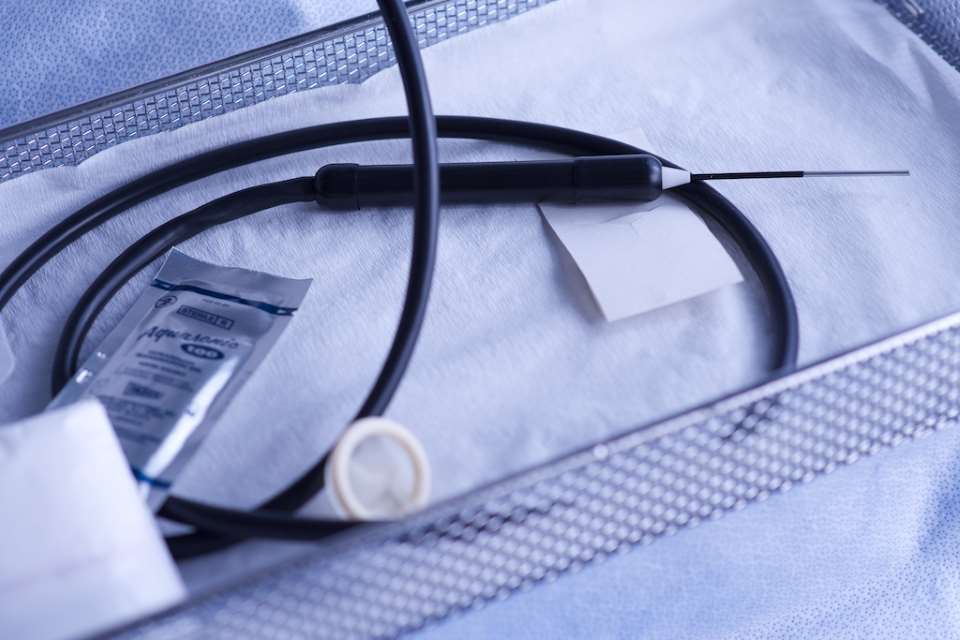 When it comes to battling cancer, innovation and evolution in medical technology play a vital role in improving treatment outcomes and patients' quality of life. One such innovation that has been making strides in recent years is cryotherapy for kidney cancer. Cryotherapy, also known as freezing therapy, cryosurgery, or cryoablation, is a cutting-edge procedure that harnesses the power of extreme cold to combat cancer cells effectively. This revolutionary technique is particularly promising for treating small, early-stage kidney cancers.
When it comes to battling cancer, innovation and evolution in medical technology play a vital role in improving treatment outcomes and patients' quality of life. One such innovation that has been making strides in recent years is cryotherapy for kidney cancer. Cryotherapy, also known as freezing therapy, cryosurgery, or cryoablation, is a cutting-edge procedure that harnesses the power of extreme cold to combat cancer cells effectively. This revolutionary technique is particularly promising for treating small, early-stage kidney cancers. At a somewhat small and unassuming airport in Maribor, Slovenia, German hydrogen propulsion startup H2FLY has quietly been building up to a major milestone in zero-emission aviation over the summer. And all the hard work has come to fruition, with the successful completion of the world’s first crewed liquid hydrogen-powered flights.
At a somewhat small and unassuming airport in Maribor, Slovenia, German hydrogen propulsion startup H2FLY has quietly been building up to a major milestone in zero-emission aviation over the summer. And all the hard work has come to fruition, with the successful completion of the world’s first crewed liquid hydrogen-powered flights.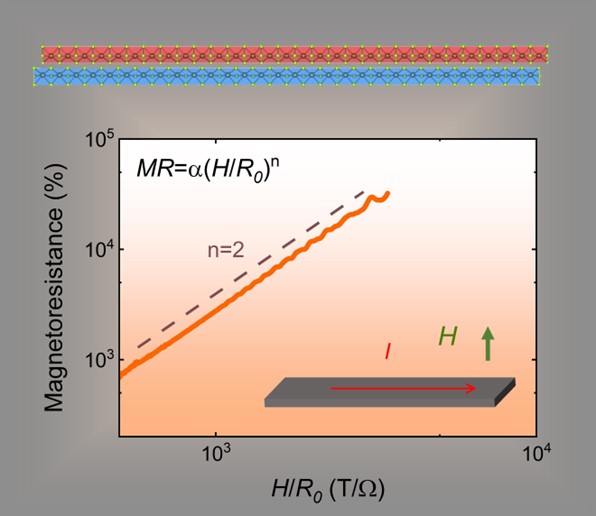 Topological effects are predicted to have many potential uses in future electronic devices. Therefore, finding ways to control these effects is desirable. As predicted by first-principles calculations, the one-dimensional (1D) transition-metal trichalcogenide TaSe
Topological effects are predicted to have many potential uses in future electronic devices. Therefore, finding ways to control these effects is desirable. As predicted by first-principles calculations, the one-dimensional (1D) transition-metal trichalcogenide TaSe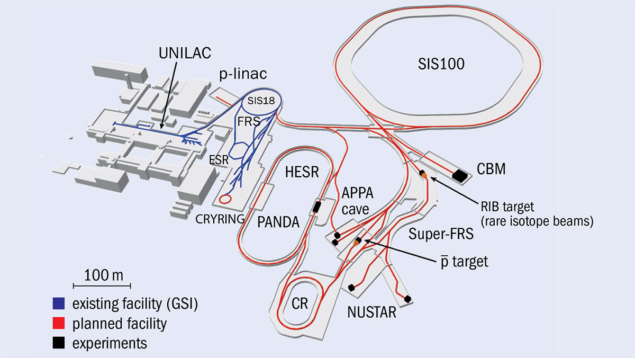 The Facility for Antiproton and Ion Research (FAIR) in Darmstadt, Germany, is embarking on a pioneering mission that will transform accelerator research and expand our understanding of the universe. With its ambitious vision to explore an extensive research canvas, FAIR is set to become a global hub for scientific exploration, spanning diverse domains such as hadron physics, nuclear structure, astrophysics, atomic physics, materials science, radiation biophysics, cancer therapy and space science.
The Facility for Antiproton and Ion Research (FAIR) in Darmstadt, Germany, is embarking on a pioneering mission that will transform accelerator research and expand our understanding of the universe. With its ambitious vision to explore an extensive research canvas, FAIR is set to become a global hub for scientific exploration, spanning diverse domains such as hadron physics, nuclear structure, astrophysics, atomic physics, materials science, radiation biophysics, cancer therapy and space science.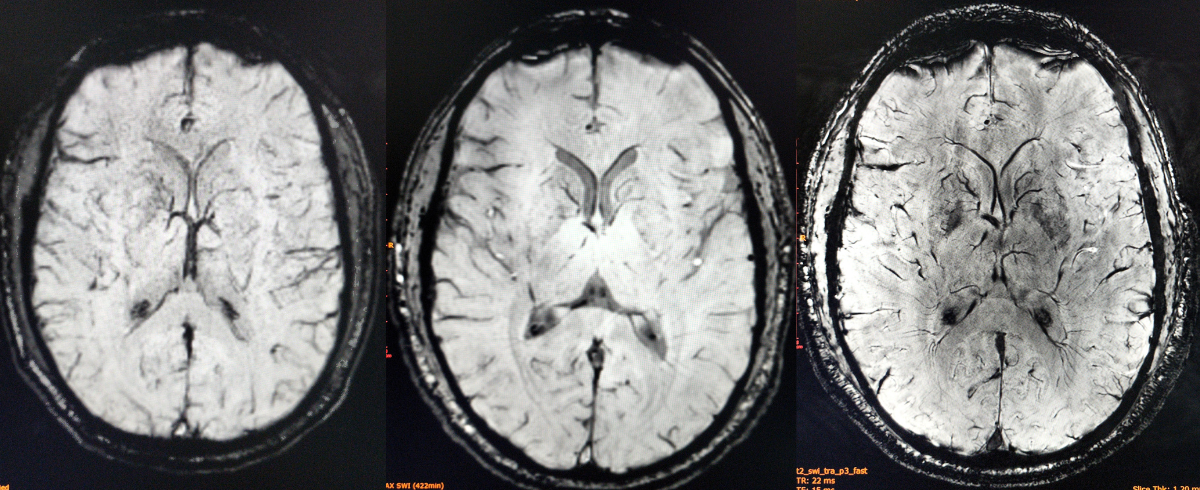 The University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign (UIUC) and Carle Health, a vertically integrated healthcare system with hospitals, physician practices and a medical school, have formed a unique partnership to co-own and operate a Siemens Healthineers MAGNETOM Terra 7 Tesla MRI scanner. This collaboration has significant implications for both research and clinical care. The scanner, with its high-powered magnetic field and advanced neuroimaging capabilities, offers transformative potential.
The University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign (UIUC) and Carle Health, a vertically integrated healthcare system with hospitals, physician practices and a medical school, have formed a unique partnership to co-own and operate a Siemens Healthineers MAGNETOM Terra 7 Tesla MRI scanner. This collaboration has significant implications for both research and clinical care. The scanner, with its high-powered magnetic field and advanced neuroimaging capabilities, offers transformative potential.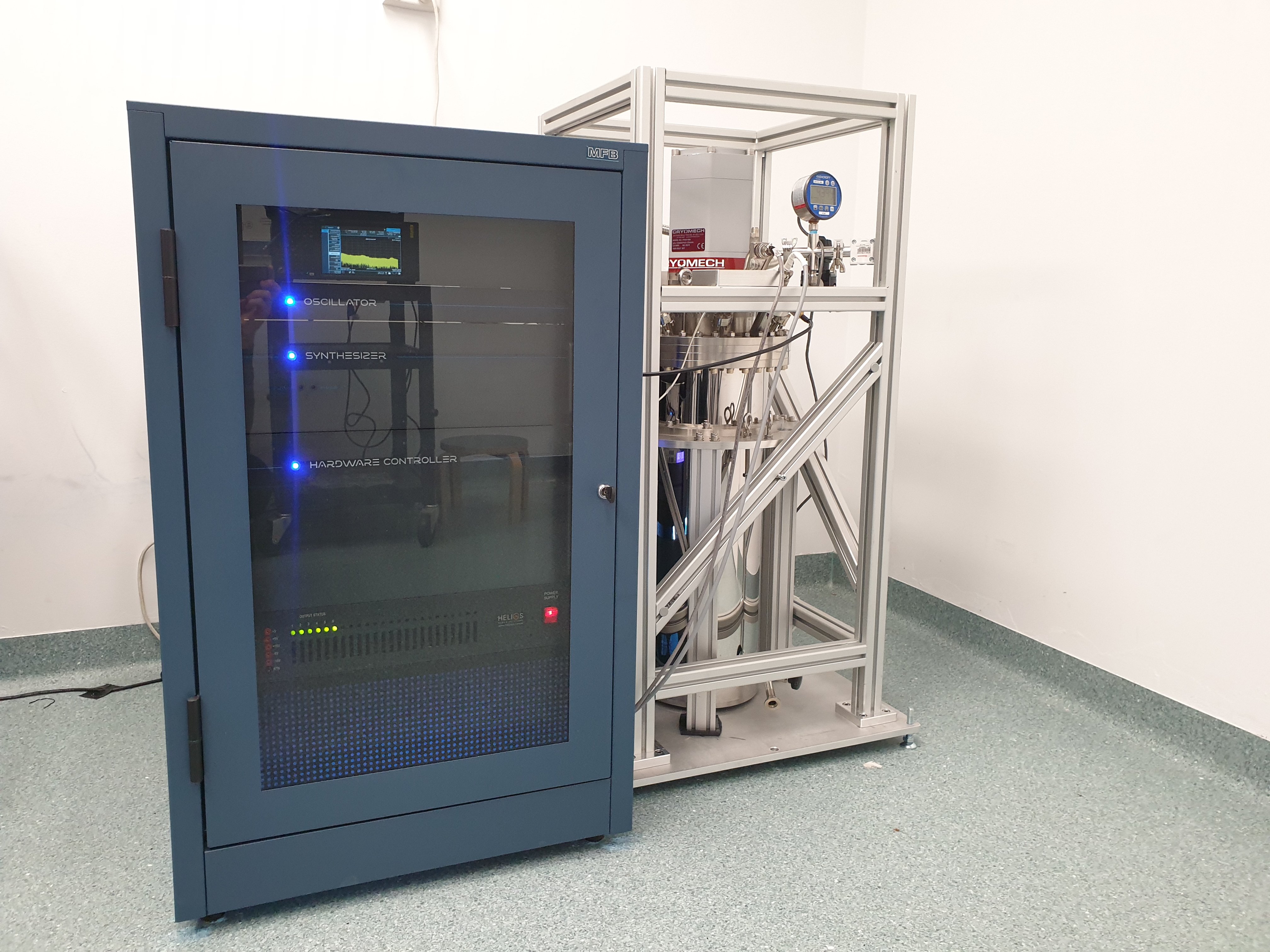 QuantX Labs, an Australian deep technology company, has achieved a groundbreaking advancement with its cryogenic sapphire oscillator, the Cryoclock. Operating at microwave frequencies, it offers unparalleled signal purity and stability, attracting interest from defense and commercial markets while also spearheading the development of advanced quantum technology for space applications.
QuantX Labs, an Australian deep technology company, has achieved a groundbreaking advancement with its cryogenic sapphire oscillator, the Cryoclock. Operating at microwave frequencies, it offers unparalleled signal purity and stability, attracting interest from defense and commercial markets while also spearheading the development of advanced quantum technology for space applications.  High-performance, highly reliable, long-lasting storage tanks for transporting hydrogen& helium molecules around the globe.
High-performance, highly reliable, long-lasting storage tanks for transporting hydrogen& helium molecules around the globe.